Discover the world of welding and its various types. From arc welding to MIG and TIG welding, each technique offers its own unique benefits and applications.
By using heat and pressure, you’ll learn how these methods join materials together, creating strong and durable bonds.
Whether you’re a beginner or an experienced welder, this article will provide you with a detailed overview of welding and its types, equipping you with the knowledge to tackle your next welding project with precision and confidence.
Key Takeaways
– Arc welding uses a high-intensity electric arc and a consumable electrode.
– MIG welding, also known as Gas Metal Arc Welding (GMAW), uses shielding gas and a consumable wire electrode.
– TIG welding requires precision and control, focusing on maintaining a steady hand, controlling the flow of filler rod, consistent arc length, and adjusting torch angle for optimal heat distribution.
– Resistance welding is a reliable and efficient method of joining materials, with high-speed production capabilities and versatile applications for joining different materials.
The Basics of Welding
You should start by familiarizing yourself with the basics of welding, such as the different types of welds and the equipment used. Welding safety is of utmost importance to prevent accidents and injuries.
Always wear protective clothing, including gloves, safety glasses, and a welding helmet with a proper shade. Ensure proper ventilation in your workspace to prevent exposure to harmful fumes and gases.
Additionally, be aware of common welding defects that can compromise the quality of your welds. These defects include porosity, which is caused by gas entrapment, and undercutting, which is the formation of a groove at the weld toe.
Understanding these basics will lay a solid foundation for your welding journey and help you produce high-quality welds safely.
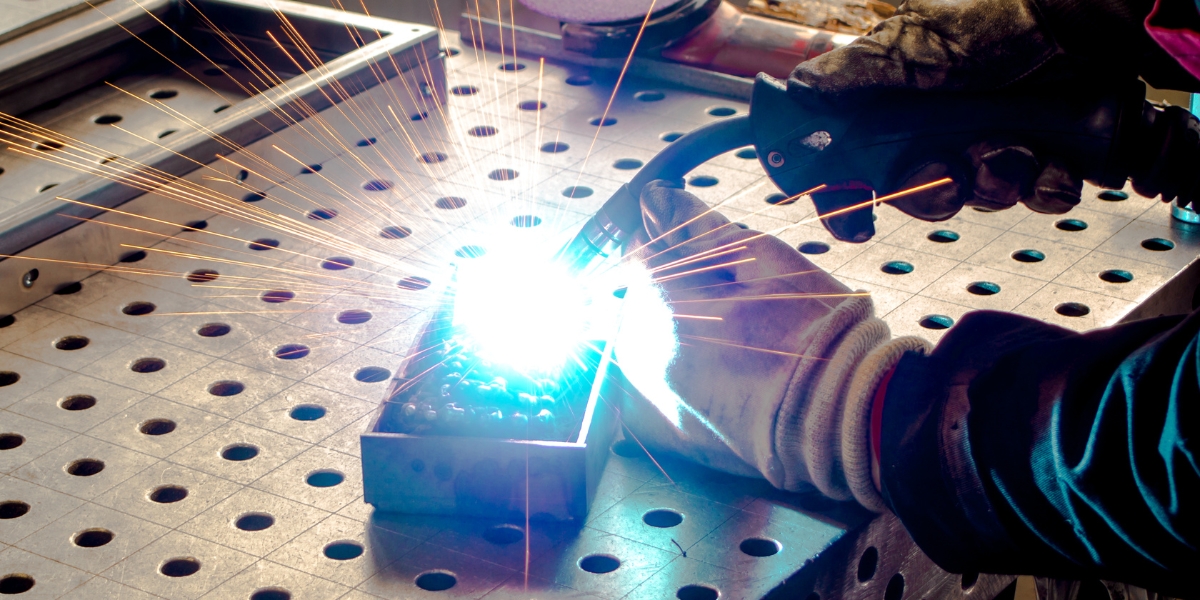
Arc Welding: A Versatile Technique
When arc welding, you can create strong and durable welds by using a high-intensity electric arc and a consumable electrode. Arc welding is a versatile technique that finds applications in various industries, including construction, automotive, and manufacturing. The benefits of arc welding include its ability to produce high-quality welds, its versatility in joining different types of metals, and its cost-effectiveness.
Arc welding offers numerous benefits, making it a preferred choice for many welding applications. Its ability to create strong and durable welds, coupled with its versatility, makes it an essential technique in various industries. Whether it’s joining metal parts in construction, automotive, or manufacturing, arc welding proves to be a reliable and cost-effective method.
Exploring MIG Welding
While exploring MIG welding, you can achieve clean and precise welds by using a shielding gas and a consumable wire electrode.
MIG welding, also known as Gas Metal Arc Welding (GMAW), is a popular welding technique that offers several advantages. One of the main advantages is its versatility, as it can be used to weld various types of metals, including steel, aluminum, and stainless steel. Additionally, MIG welding allows for high welding speeds, which increases productivity. The technique is also relatively easy to learn and use, making it suitable for both beginners and experienced welders.
However, there are some disadvantages to consider. MIG welding requires the use of shielding gas, which can add to the overall cost of the process. It also produces a significant amount of heat, which can distort the material being welded.
Overall, MIG welding techniques offer a balance between efficiency and precision, making it a popular choice in various industries.
TIG Welding: Precision and Control
To achieve precision and control in TIG welding, you can focus on maintaining a steady hand and controlling the flow of the filler rod. Precision welding requires advanced techniques that involve careful attention to detail and a thorough understanding of the welding process.
One key aspect is maintaining a consistent arc length, which ensures that the heat input remains constant and promotes even penetration. Additionally, controlling the travel speed is crucial to achieve uniform bead width and prevent overheating.
Another important factor is the angle of the torch, which affects the shape and penetration of the weld. By adjusting the torch angle, you can optimize the heat distribution and create strong, precise welds.
Lastly, proper shielding gas flow and coverage are essential to protect the weld pool and ensure clean, defect-free welds.
Uniting Materials With Resistance Welding
You can effectively unite materials through resistance welding, providing a reliable and efficient method of joining. Resistance welding applications are widespread in various industries due to their numerous advantages. These include:
– High-speed production: Resistance welding enables quick and continuous joining of materials, making it ideal for mass production.
– Strong and consistent joints: The heat generated during resistance welding creates a metallurgical bond, resulting in strong and reliable joints.
– Versatile applications: Resistance welding can be used to join a wide range of materials, including metals, plastics, and even dissimilar materials.
However, resistance welding also has its disadvantages:
– Limited joint thickness: Resistance welding is most effective for thin to medium thickness materials. Thick joints may require multiple passes or alternative methods.
– Complexity of setup: Proper equipment and expertise are needed to set up and maintain resistance welding machines, which can be costly and time-consuming.
– Heat affected zone: The intense heat generated during resistance welding can cause distortion and weaken the surrounding material.
Overall, resistance welding offers a reliable and efficient method of joining materials, with its advantages outweighing the disadvantages in many applications.

Frequently Asked Questions
What Are the Common Safety Precautions to Take While Welding?
When welding, it is crucial to prioritize safety. Ensure you have the necessary safety equipment, such as gloves, goggles, and a welding helmet. Familiarize yourself with proper welding techniques to minimize risks and accidents.
How Can I Choose the Right Welding Method for My Project?
To choose the right welding method for your project, consider factors like material type, thickness, and desired weld quality. Research the pros and cons of different techniques such as MIG, TIG, and stick welding to make an informed decision.
What Are the Main Differences Between MIG and TIG Welding?
When comparing MIG and TIG welding, it’s important to consider their differences. MIG welding is faster and easier, but TIG welding offers higher quality and precision. Each method has its advantages and disadvantages.
Can Welding Be Done on All Types of Metals?
Yes, welding can be done on various types of metals. However, it is important to consider metal compatibility as certain metals may have limitations when it comes to welding processes.
Are There Any Specialized Certifications or Training Required to Become a Professional Welder?
To become a professional welder, specialized certifications and training are required. These include welding certifications and completion of welding training programs. These qualifications ensure that you have the necessary skills and knowledge for a successful welding career.
Conclusion
In conclusion, welding is a versatile and precise technique used to unite materials through various methods such as arc welding, MIG welding, TIG welding, and resistance welding.
Each method offers its own advantages and is suitable for different applications.
By understanding the basics of welding and its different types, one can achieve precision and control in joining materials effectively.
The wide range of options available in welding allows for flexibility and adaptability in various industries and projects.

